Squamous Cell Carcinoma FAQs
What is squamous cell carcinoma? »
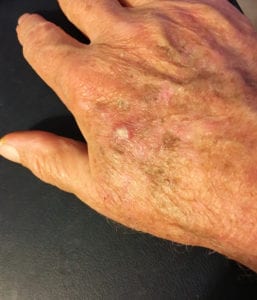 Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common form of skin cancer. It forms in the squamous cells that make up the middle and outer layer of the skin. Most squamous cell carcinomas result from prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or tanning beds or lamps. Unlike basal cell carcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas can occur in more wide-ranging locations. Although more common on the sun-exposed skin on the backs of the hands, the ears, the scalp, and the lips, this form of skin cancer can occur anywhere on the body, including inside the mouth and on the genitals. Not considered life threatening if treated early, like basal cell carcinoma, it can also be disfiguring. If it spreads, it can be life threatening.
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common form of skin cancer. It forms in the squamous cells that make up the middle and outer layer of the skin. Most squamous cell carcinomas result from prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or tanning beds or lamps. Unlike basal cell carcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas can occur in more wide-ranging locations. Although more common on the sun-exposed skin on the backs of the hands, the ears, the scalp, and the lips, this form of skin cancer can occur anywhere on the body, including inside the mouth and on the genitals. Not considered life threatening if treated early, like basal cell carcinoma, it can also be disfiguring. If it spreads, it can be life threatening.
What do squamous cell carcinomas look like? »
Squamous cell carcinomas appear as red scaly patches, scaly bumps, or open sores. Left alone, they become larger and destroy tissue on the skin. They can also spread to other areas of the body.
What causes squamous cell carcinomas? »
Squamous cell carcinomas of the skin develop when the flat, thin squamous cells in the outer layer of the skin develop errors in their DNA. In ordinary, healthy skin, new cells push older cells toward the skin surface, where they die and are shed. When the DNA is damaged, the squamous cells instead grow out of control, forming a squamous cell carcinoma.
What are the signs of squamous cell carcinoma? »
 Squamous cell carcinomas are more typical on sun-exposed skin: the scalp, the backs of the hands, the ears, and the lips. But this form of skin cancer can spread anywhere on your body.
Squamous cell carcinomas are more typical on sun-exposed skin: the scalp, the backs of the hands, the ears, and the lips. But this form of skin cancer can spread anywhere on your body.
Squamous cell carcinomas will have these characteristics:
- A firm, red nodule
- A flat sore with a scaly crust
- A new sore or raised area on an old scar
- A rough, scaly patch on your lip that can become an open sore
- A red sore or rough patch inside your mouth
- A red, raised patch or wart-like sore on or in the anus or on the genitals
What are the stages of Squamous Cell Carcinoma?
There are five stages of this form of skin cancer:
Most squamous cell carcinomas show up as Stage 0 or Stage 1.
- Stage 0 — Also known as carcinoma in situ, this stage is not considered to be invasive. The abnormal cells are only in the upper layer of the epidermis, the outer skin.
- Stage 1 and Stage 2 — Designation in these stages depends on how big the cancer is and if there are any high-risk features in the tumor.
- Stage 3 — This stage has spread to areas below the skin, such as into the lymph nodes or other local structures like muscle, bone, or cartilage.
- Stage 4 — The cancer has spread to distant sites in this stage.
What are the different types of Squamous Cell Carcinoma?
People assume there is just a single type of squamous cell carcinoma, but there are actually several different types. Some are more likely to spread than others, but in general, most types share similar characteristics. The primary difference between the following types is related to the unique characteristics of the cancerous cells.
The primary types of squamous cell carcinoma are:
- Adenoid/pseudoglandular squamous cell carcinoma
- Intraepidermal squamous cell carcinoma
- Large cell keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma
- Large cell nonkeratinizing squamous cell carcinoma
- Lymphoepithelial carcinoma
- Papillary squamous cell carcinoma
- Papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Small cell keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma
- Spindle cell squamous cell carcinoma
- Verrucous squamous cell carcinoma
How aggressive is Squamous Cell Carcinoma?
Squamous cell carcinoma is not often considered to be life threatening. This form of skin cancer that affects the squamous cells tends to create slow-growing tumors. Although squamous cell carcinoma is more likely to invade deeper layers of the skin and spread to other parts of the body than basal cell carcinoma, this is still uncommon.
Only about 5 to 10 percent of squamous cell carcinoma tumors are considered to be “aggressive.”
How fast do Squamous Cell Carcinoma lesions grow?
As mentioned above, these are typically very slow-growing tumors. There can be exceptions to this in from 5 to 10 percent of cases, but generally their slow growth makes squamous cell carcinoma easy to diagnose and treat successfully.
How are squamous cell carcinomas treated? »
The methods for treating squamous cell carcinomas are the same as for basal cell carcinomas:
Treatment Through Surgery
Electrodesiccation and curettage — A curette is used to scrap out the growth, then the base is seared with an electric needle to close the blood vessels and destroy any remaining cancer cells. The squamous cell growth needs to be very small for this method to be used.
Surgical excision — This involves cutting out the cancerous lesion with a scalpel, along with a margin of healthy skin around it. This is called wide excision.
Cryosurgery — Small, superficial squamous cell carcinomas can be frozen with liquid nitrogen.
Mohs surgery — This method has the highest success rate of removing all of the squamous cell carcinoma. Your surgeon removes the squamous cell cancer layer by layer or ring by ring around the growth. After a layer is removed, it is examined immediately to check for any remaining cancer cells on the borders. If cancer cells are still found, another layer or ring is removed. This process is continued until the sample shows itself to be clean. This is especially effective for removing growths on the lips, as only the minimum amount of tissue is removed.
treatment through Drugs
Although the squamous cell carcinoma needs to be relatively small and superficial, topical treatments can be successful. These drugs work by inflaming the area where they are applied. The body responds by sending white blood cells to attack the inflammation. These white blood cells go after the mutated basal cells. Aldara, Efudex, and Fluoroplex are three of the most used drugs.
Do you need Chemotherapy for Squamous Cell Carcinoma?
Because just about all squamous cell carcinoma is usually localized it is typically not treated with chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is used for widespread cancer cell eradication, not localized growths. Chemotherapy could be used for a very small percentage of these cases, typically if the cancer has spread.
About 95 percent of squamous cell carcinomas are detected early, and this makes them easy to treat. All treatment options are highly successful, but Mohs micrographic surgery is the most successful while taking the least amount of healthy skin.
What is the success rate for treating squamous cell carcinoma? »
Unlike basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma tends to be more invasive and is likely to spread if left untreated. As with basal cell carcinoma, Mohs micrographic surgery has the best success rates, at 97 percent. Excision has a 92 percent success rate. For low-risk, small tumors, curettage, and electrodesiccation is successful in 96 percent of cases, but it cannot be used for larger, deeper growths.
Squamous cell carcinoma is generally not considered life-threatening if treated early. However, if left untreated, squamous cell carcinoma can spread and it can then become life-threatening. Reliable statistics are not available, however, because most of these cancers are treated in a dermatologist’s office
How Can I Prevent Skin Cancer? »
The best way to prevent skin cancer is with prevention. Even if it is cloudy outside, you still need to wear sunscreen. Choose one that is at least 30 SPF, and apply to all exposed areas of skin. You should also wear a hat to protect your scalp, back of neck, and the tops of ears. You also need to avoid using tanning beds, which are known to emit cancer-causing UV rays. In addition, you need to perform regular at-home skin checks. Look for any changing moles or lesions that look irregular. You should also schedule regular clinical skin checks as well.
Do Genetics Play A Role? »
While genetics can play a role in the development of certain types of cancer, lifestyle choices and lack of proper skin checks are the leading cause of squamous cell carcinoma. That is why it is so important to wear sunscreen and keep an eye out for changing moles and new skin lesions.
Are Certain People More High-Risk Than Others? »
Yes, some people may be at higher risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma than others. These include individuals who work outdoors or spend a lot of time outside without proper sun protection. Individuals who use tanning beds are also at higher risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma than those who do not.
Where Can I Find More Information About Squamous Cell Carcinoma? »
You can ask your general medical doctor and your dermatologist about the prevention and treatment of squamous cell carcinoma. You can also look online at the American Cancer Society for more information. You can find a wealth of information about early detection, prevention, and treatment of squamous cell carcinoma.
Are there Vaccines That Prevent Squamous Cell Carcinoma? »
No, currently there are no vaccines available that prevent squamous cell carcinoma. The only way to prevent SCC is to protect your skin when you are outside, avoid tanning bed use, and perform regular skin checks.

Start Your Treatment For Squamous Cell Carcinoma Today »
If you’re interested in learning more about squamous cell carcinoma or would like to schedule your first treatment, please click the button below to find a Mohs Surgeon near you.


